Rapid advancements in genomics have had a transformative impact across various fields, from deepening our understanding of disease and developing innovative treatments to enhancing agriculture and personalized medicine.
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has provided comprehensive insights into genome structure and genetic variations, facilitating studies on rare genetic diseases and cancer genomics1. Meanwhile, single-cell genomics has offered critical insights into tissue heterogeneity and cellular mechanisms2. Integrating advanced AI and analytical tools with genomics has enhanced risk prediction and the precision of genomic studies3.
Automation and automated liquid handling have significantly advanced genomics by improving efficiency, accuracy, and throughput in various workflows, while magnetic bead cleanup solutions support researchers in achieving high-quality samples4,5.
In this article, we will explore the critical role of liquid handlers in genomics, introduce DISPENDIX’s I.DOT Liquid Handler and G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device, and demonstrate how they can help you transform your genomics workflows!
The Role of Liquid Handlers in Genomics
Genomics workflows involve numerous steps requiring the transfer of tiny liquid volumes, a challenge that becomes more pronounced as the number of samples increases. It’s no secret that manual pipetting is prone to human error, which can compromise the quality and integrity of resulting samples and data6. This issue is especially problematic in highly sensitive genomics workflows, where small variations in reagent concentrations or pipetting accuracy can lead to experiment failure and unusable data — a scientist’s nightmare.
Liquid handlers play a crucial role in improving the efficiency, reliability, and flexibility of genomics workflows, enhancing the overall quality and throughput of genomic research7,8. Automated liquid handlers save valuable time, minimize waste, and cut costs by reducing the need for unnecessary experimental repeats. They also eliminate contamination risks and improve sample quality through advanced magnetic bead cleanup solutions. Moreover, they increase reproducibility, addressing the reproducibility crisis faced by researchers today9.
The I.DOT Liquid Handler: Enhancing Dispensing Accuracy & Workflow Efficiency
The I.DOT Liquid Handler is an advanced liquid dispensing tool designed for high-throughput, precise liquid handling across various scientific applications, including genomics (Fig. 1). Utilizing droplet-based, non-contact dispensing technology, it ensures exceptional accuracy, speed, and reduced reagent consumption. Key features of the I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser include:
- High Throughput: Efficiently dispenses into 96-, 384-, and 1536-well plates.
- Flexible Volume Range: Handles volumes from 8 to 50 nanoliters.
- Non-Contact Dispensing: Eliminates pipette tips, reducing contamination and consumable costs and improving lab sustainability.
- DropDetection Technology: Integrated volume verification provides precise droplet control for reproducibility.

Figure 1. The I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser is equipped with innovative technology, making it sure to improve the accuracy, efficiency, and reliability of your genomics workflows.

The G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device: Ensuring Pristine Samples
The G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device is an advanced magnetic bead cleanup instrument designed to purify NGS libraries by removing contaminants and ensuring high-quality samples for downstream applications (Fig. 2). Key features and benefits include:
- Magnetic Bead Cleanup: Ensures high-purity nucleic acid recovery.
- Automated Workflow Integration: Seamlessly integrates into existing lab automation systems, including liquid handlers like the I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser.
- High Throughput Capability: Processes multiple samples simultaneously for increased productivity.
- User-Friendliness: Intuitive software simplifies operation and reduces hands-on time.

Figure 2. The G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device supports the purification of NGS libraries for high-quality samples and results you can trust.
Integration of the I.DOT & the G.PURE in Genomic Workflows
The DISPENDIX I.DOT Liquid Handler and the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device work together to streamline genomic workflows such as NGS library preparation and qPCR plate preparation by combining precise liquid handling with efficient sample purification via magnetic bead cleanup (Table 1). The I.DOT Liquid Handler ensures accurate and reproducible dispensing of reagents and samples, accommodating various volumes and liquid types, which is crucial for setting up genomic assays and high-throughput sequencing projects. Meanwhile, the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device efficiently removes contaminants from NGS libraries, delivering high-purity nucleic acids for sequencing.
Table 1. Comparison of the I.DOT/G.PURE bundle against other liquid handling methods.
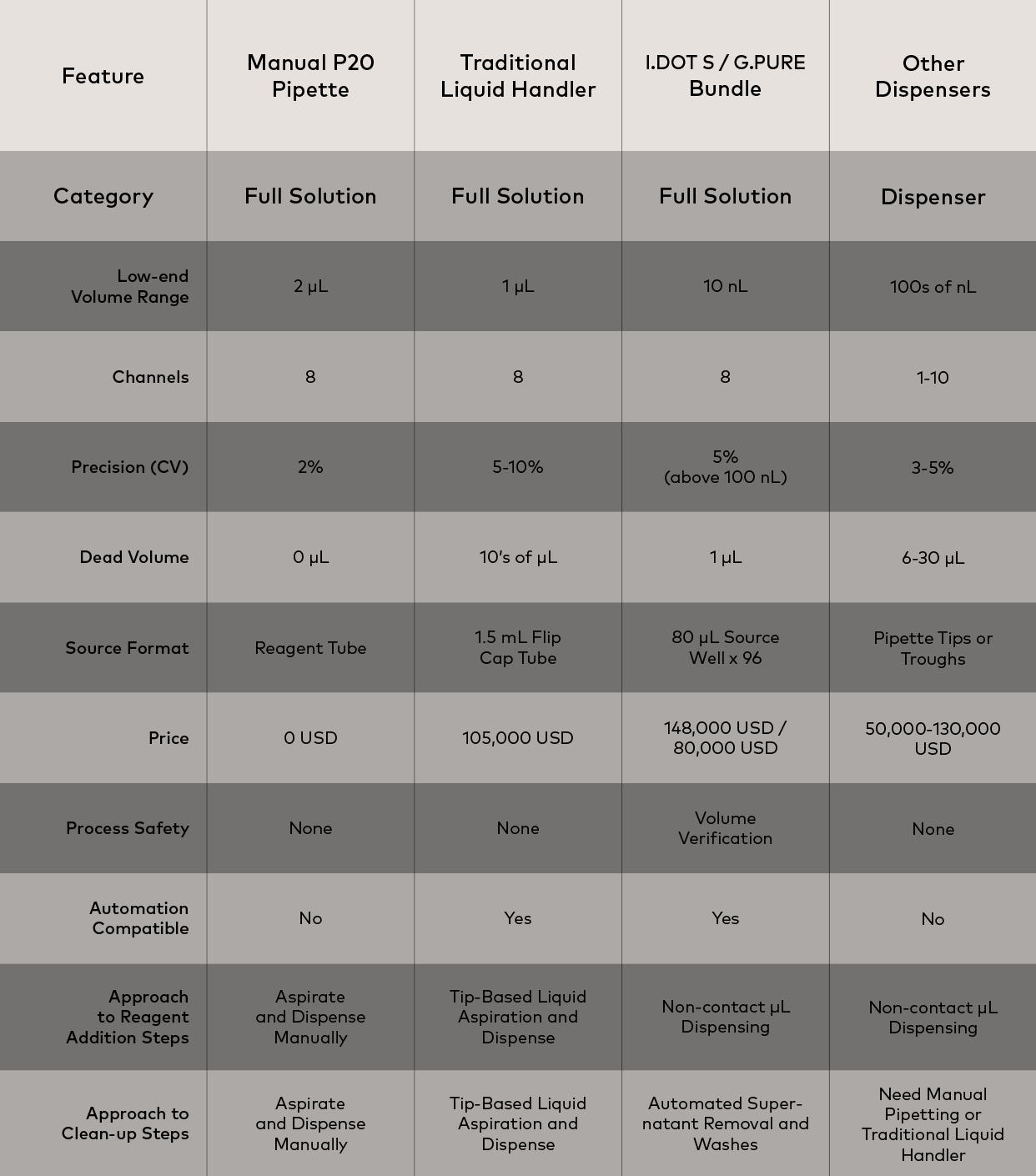
Together, these devices enhance workflow efficiency by reducing hands-on time and speeding up sample preparation and purification processes. The I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser’s automated dispensing and the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device’s high-throughput purification capabilities significantly cut down manual handling and the potential for human error, leading to faster turnaround times. Additionally, the combination ensures tip-top sample quality with precise reagent volumes and magnetic bead cleanup, resulting in contaminant-free nucleic acids and more consistent and reliable sequencing outcomes.
Conclusion
The rapid advancements in genomics have revolutionized various fields, with innovations like NGS and single-cell genomics providing deep insights into cellular heterogeneity and disease mechanisms. Automated liquid handling systems, such as the I.DOT Liquid Handler and the magnetic bead cleanup-based G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device play a crucial role by combining precise, high-throughput dispensing with efficient sample purification. These technologies enhance workflow efficiency, accuracy, and sample quality, reducing hands-on time and minimizing human error.
Join countless researchers who trust the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device for their sample purification needs. Enhance your results, save time, and focus on what truly matters — your groundbreaking research. Our state-of-the-art magnetic bead cleanup solution ensures that you achieve pristine, high-purity samples every time, making your research faster, easier, and more reliable. Book a demo today!
References
- Satam H, Joshi K, Mangrolia U, et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology. 2023;12(7):997. doi:10.3390/biology12070997
- Deutsch A, Feng D, Pessin JE, Shinoda K. The Impact of Single-Cell Genomics on Adipose Tissue Research. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(13):4773. doi:10.3390/ijms21134773
- Lin J, Ngiam K. How data science and AI-based technologies impact genomics. Singapore Med J. 2023;64(1):59. doi:10.4103/singaporemedj.SMJ-2021-438
- Tegally H, San JE, Giandhari J, De Oliveira T. Unlocking the efficiency of genomics laboratories with robotic liquid-handling. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):729. doi:10.1186/s12864-020-07137-1
- Gaisford W. Robotic Liquid Handling and Automation in Epigenetics. SLAS Technol. 2012;17(5):327-329. doi:10.1177/2211068212457160
- Guan XL, Chang DPS, Mok ZX, Lee B. Assessing variations in manual pipetting: An under-investigated requirement of good laboratory practice. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2023;30:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.jmsacl.2023.09.001
- Meldrum D. Automation for Genomics, Part One: Preparation for Sequencing. Genome Res. 2000;10(8):1081-1092. doi:10.1101/gr.101400
- Meldrum D. Automation for Genomics, Part Two: Sequencers, Microarrays, and Future Trends. Genome Res. 2000;10(9):1288-1303. doi:10.1101/gr.157400
- Baker M. 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature. 2016;533(7604):452-454. doi:10.1038/533452a