Recent advancements in methodologies and technology have led to the increased prominence of miniaturized reactions. These reactions retain accuracy and reproducibility while scaling down the assay to substantially reduce the total volume. Miniaturized reactions are being utilized in many areas of scientific research, including drug discovery1 and diagnostics2. Miniaturization is transforming research, enabling increased throughput, reagent conservation, time efficiency, and cost-saving3. In this article, we will discuss the main challenges in traditional experimental workflows, how miniaturization provides the solution to many of these issues, and how DISPENDIX can help fulfill your miniaturization and automation needs.
Challenges in Traditional Laboratory Workflows
Reagent Waste
Scientific research generally involves vast amounts of waste, with detrimental effects on both lab efficiency and the environment4. Many experiments require relatively high volumes of reagents and samples in order to produce valid results. The inefficiencies of manual experiments, such as high dead volumes, result in precious samples or expensive reagents being wasted, limiting their use across multiple experiments and decreasing lab output5. Furthermore, each individual experiment generally requires hundreds of plastic pipette tips, which cannot be recycled and often need autoclaving due to biological contamination. This not only increases the lab costs required to continually replace tips but also increases the lab’s carbon footprint and contributes to global warming6. One study estimated that labs around the world produced approximately 5.5 million tonnes of single-use plastic waste, amounting to ~2% of the global plastic waste that year7.
Manual Errors
Human error further contributes to lab inefficiencies and high costs. The ever-increasing intricacy of experimental workflows can increase the likelihood of human error. Errors can occur at any stage in the experiment but are particularly common when repetitive, labor-intensive processes are being carried out, such as pipetting samples (Fig. 1) and carrying out wash steps8. Experimental errors affect the accuracy of experimental data, impacting not only the validity of the results but also the reproducibility of experiments. Reproducibility is a growing crisis in science, with one survey finding that 70% of researchers have tried and failed to replicate another scientist’s results, and over 50% have failed to reproduce their own results9.
Figure 1. Manual pipetting is error-prone, decreasing the accuracy and reliability of results and wasting reagents.
Low Throughput
High-throughput experimentation is becoming an essential aspect of biology because it enables researchers to simultaneously run experiments using high numbers of samples to accelerate discovery and optimization10. Conversely, low-throughput experiments are time-consuming and resource-intensive, making scaling these experiments up expensive.
Miniaturized Reactions: A Game-Changer
Miniaturized reactions are solving many of the challenges seen in traditional experimental workflows. They use volumes in the nanoliter range, therefore decreasing the volumes of samples and reagents needed to produce the same (or increased) amounts of data11. This reduction in the volumes of reactants required for miniaturized reactions enables higher throughput experiments and high scalability due to a reduction in associated costs3. The use of lower volumes of starting material also results in a decrease in the amount of hazardous waste produced11.
Lowering the volumes of reagent being pipetted increases the risk of manual error and decreases reliability; however, automated miniaturized reactions remove human error, improving experimental precision, data validity, and, ultimately, reproducibility. The removal of human error also saves money as fewer experiments have to be scrapped, resulting in a decrease in the wastage of expensive samples, reagents, and equipment. In addition, the reproducibility of automated miniaturized reactions decreases any batch effects arising from differences in sample preparation between researchers – such as manual pipetting variation12 – enabling the successful scaling up of experiments. Therefore, combining reaction miniaturization with automation further increases lab efficiency and experimental accuracy13.
DISPENDIX Solutions
At DISPENDIX, we are passionate about enabling miniaturized reactions and have developed solutions that can miniaturize complex workflows without affecting the quality of the data produced – with the ability to scale down to 10% of the manufacturer’s recommended volumes. The accuracy of the I.DOT Liquid Handler is such that reagents in the miniaturized reaction can be dispensed with only 1 μL of dead volume and to a resolution of 0.1 nL. This automation decreases the volume of precious samples or expensive reagents wasted and thus increases the cost-effectiveness of experiments. The use of DISPENIX’s automated solutions reduces human pipetting errors and can even provide insight into the exact volume of reagent dispensed into each well, using the integrated volume verification technology, ensuring accuracy and data validity. In addition, the contact-free nature of the dispenser results in the use of a fraction of the pipette tips compared to traditional automation dispensing methods, saving money and practicing effective sustainability by reducing the amount of waste plastic produced (Fig. 2).
DISPENDIX’s G.PREP ROI calculator can be used to assess how much money your lab can save by utilizing the G.PREP NGS Automation Bundle to decrease consumable use and miniaturize reactions. The optimization of miniaturized reaction workflows is key to their successful implementation. In addition to providing the technology needed to carry out miniaturized reactions, DISPENDIX eliminates any worries about method optimization by carrying out the R&D to ensure that you generate a trustworthy miniaturized reaction. The reproducibility, precision, speed of dispense, and reduced reagent volumes required in miniaturized reactions using DISPENDIX’s solutions enable assays to be scaled up and high-throughput experiments to be carried out in a cost- and time-efficient manner.

Figure 2. The I.DOT Liquid Handler uses contact-free technology to add samples and reagents to plates accurately and without the use of plastic pipette tips.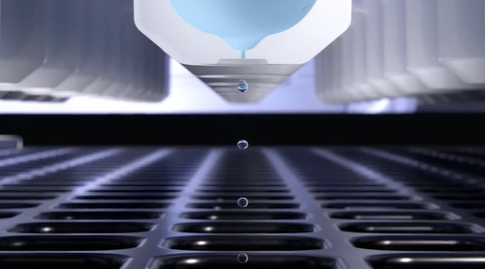
Conclusion
Lab inefficiencies waste precious funds and can lead to a loss of data accuracy, validity, and reproducibility. The miniaturization of experiments is solving many of these challenges associated with traditional experimentation. Miniaturized reactions use very small volumes of samples and reagents, thus reducing costs and enabling scalability. The combination of miniaturized reactions and automated liquid dispensing, such as that offered by DISPENDIX’s suite of technologies, reduces human error to improve precision and reproducibility, decreases plastic waste for enhanced sustainability, and saves users money.
Ready to accelerate your research?
Discover how DISPENDIX can enhance precision, efficiency, and reproducibility in your lab through our miniaturization technology. Download the I.DOT brochure or the G.PREP brochure and take the next step in transforming your workflows!
References
- Carstens C, Elbracht R, Gärtner C, Becker H. Opportunities and limits of cell-based assay miniaturization in drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2010;5(7):673-679. doi:10.1517/17460441.2010.488264
- Natalia A, Zhang L, Sundah NR, Zhang Y, Shao H. Analytical device miniaturization for the detection of circulating biomarkers. Nat Rev Bioeng. 2023;1(7):481-498. doi:10.1038/s44222-023-00050-8
- Pereira SAP, Dyson PJ, Saraiva MLMFS. Miniaturized technologies for high-throughput drug screening enzymatic assays and diagnostics – A review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2020;126:115862. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2020.115862
- Opperman CJ, Singh S, Barton F. Appropriate disposal of waste in the laboratory: Neglected but not forgotten. Afr J Lab Med. 2022;11(1):1786. doi:10.4102/ajlm.v11i1.1786
- Silva TC, Eppink M, Ottens M. Automation and miniaturization: enabling tools for fast, high-throughput process development in integrated continuous biomanufacturing. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2022;97(9):2365-2375. doi:10.1002/jctb.6792
- Penndorf P. Reducing plastic waste in scientific protocols by 65% — practical steps for sustainable research. FEBS Lett. 2024;598(11):1331-1334. doi:10.1002/1873-3468.14909
- Urbina MA, Watts AJR, Reardon EE. Labs should cut plastic waste too. Nature. 2015;528(7583):479-479. doi:10.1038/528479c
- Hentz NG, Knaide TR. Effect of Liquid-Handling Accuracy on Assay Performance. SLAS Technol. 2014;19(2):153-162. doi:10.1177/2211068213504095
- Baker M. 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature. 2016;533(7604):452-454. doi:10.1038/533452a
- Mennen SM, Alhambra C, Allen CL, et al. The Evolution of High-Throughput Experimentation in Pharmaceutical Development and Perspectives on the Future. Org Process Res Dev. 2019;23(6):1213-1242. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.9b00140
- Gesmundo N, Dykstra K, Douthwaite JL, et al. Miniaturization of popular reactions from the medicinal chemists’ toolbox for ultrahigh-throughput experimentation. Nat Synth. 2023;2(11):1082-1091. doi:10.1038/s44160-023-00351-1
- Guan XL, Chang DPS, Mok ZX, Lee B. Assessing variations in manual pipetting: An under-investigated requirement of good laboratory practice. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2023;30:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.jmsacl.2023.09.001
- Kushiro K, Carter M, Kinman J, Fox D, Madamba N, Strycharz J. Streamlining your miniaturized library prep with automation for high-throughput applications. J Biomol Tech JBT. 2020;31(Suppl):S11.