Semi-automated pipetting systems are essential lab tools that bridge the gap between manual pipetting and fully automated liquid handling robots, offering scientists a balance of control and automation in experimental workflows. Semi-automated pipetting solutions have substantial benefits over manual pipetting, including improved accuracy and precision for more reproducible workflows and enhanced data integrity, especially in omics applications1. Moreover, semi-automation improves workflow scalability, which is essential in high-throughput screening (HTS) applications such as compound testing for drug discovery. Advanced semi-automated pipetting systems integrate tip-free technology and facilitate assay miniaturization, reducing costs and improving sustainability. Here, we will explore the different types of semi-automated pipetting solutions and their applications.
Types of Semi-Automated Pipetting Solutions
From speeding up experiments to reducing errors, these handy semi-automated pipetting tools come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each uniquely tailored to enhance different aspects of experimental workflows:
Electronic Pipettes With Multichannel Heads
Electronic pipettes with multichannel heads represent an advanced semi-automated pipetting solution that couples the enhanced accuracy and ergonomic benefits of electronic pipettes with multichannel systems' improved efficiency and scalability. They can have multiple channels (ranging from 8 to 384), enabling the parallel processing of numerous samples, which is particularly useful for high-throughput experiments. In addition, many electronic pipettes can be programmed to perform multiple dispensing, diluting, and mixing automatically, which reduces the need for manual adjustments.
Advanced tipless and non-contact multichannel liquid dispensers, like the I.DOT Liquid Handler (Fig. 1), provide even more benefits. The I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser’s tipless nature saves costs and reduces plastic waste, while its unique dispensing setup curbs the risk of cross-contamination, and integrated volume verification technology helps with error recovery.
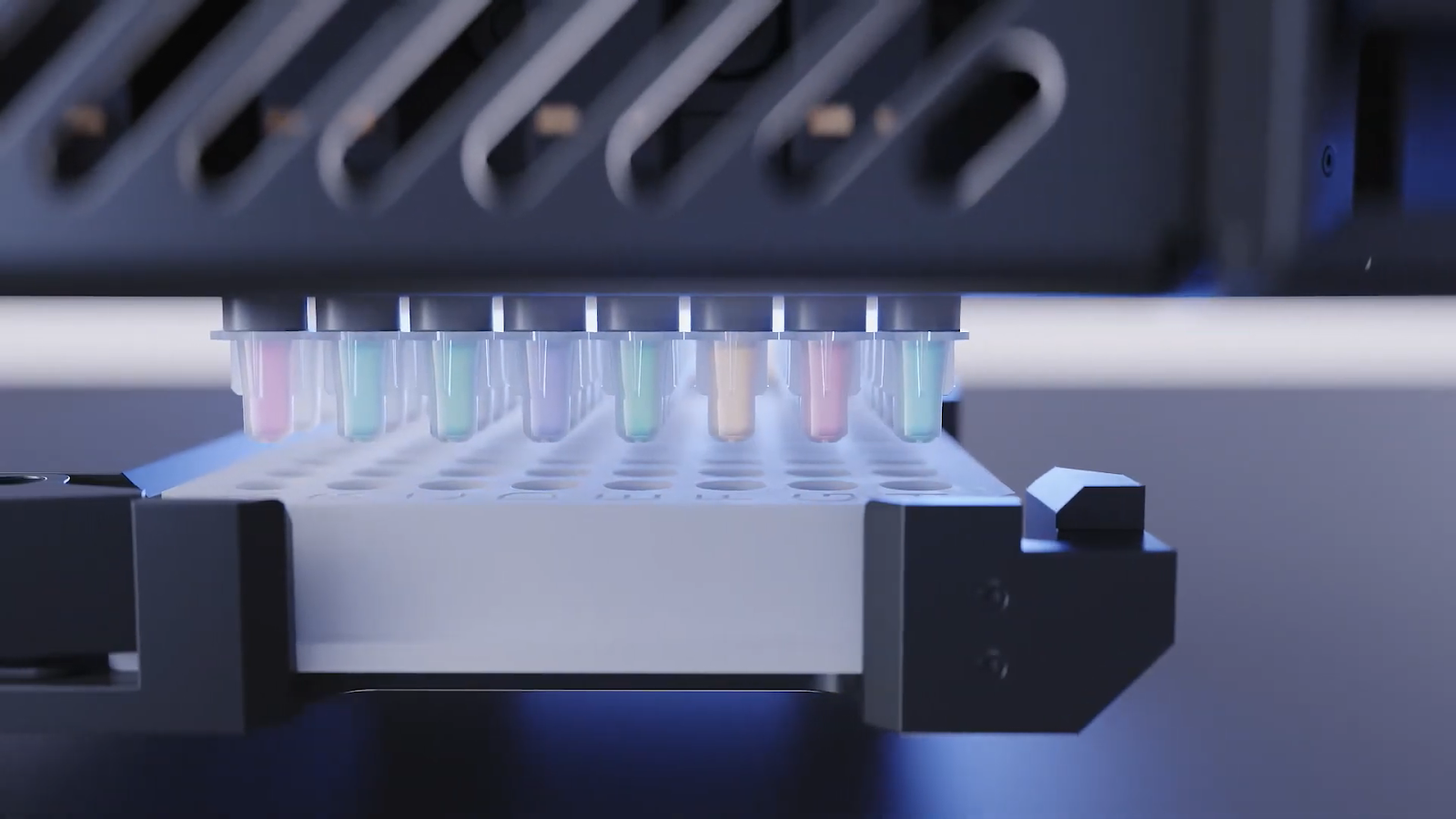
Figure 1. DISPENDIX’s I.DOT Non-Contact Liquid Dispenser is perfect for the economical, eco-conscious scientist.
Liquid Handling Robots With Manual Control
This innovative semi-automated pipetting solution combines robotic arm movement with manual pipette control for a more flexible, programmable option. These systems effectively couple the precision and efficiency of automated liquid handling with the flexibility and control afforded by manual intervention. This enables users to optimize their workflows for various applications, ensuring high throughput and adaptability to specific experimental needs2. These hybrid systems are especially useful for assisting with repetitive tasks and can often be integrated with other lab equipment.
By teaming up these robotic arms with other semi-automated pipetting systems, such as multichannel liquid dispensers and other lab devices, researchers can achieve streamlined experiments and a seamlessly integrated workflow. For example, the G.STATION NGS Workstation (Fig. 2) combines the L.DROP Robotic Arm with the I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser and the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device for complete next-generation sequencing (NGS) library prep automation. This comprehensive solution allows users to program automated reagent dispensing, bead-based clean-ups, and sample transfers – all in a temperature-controlled environment.
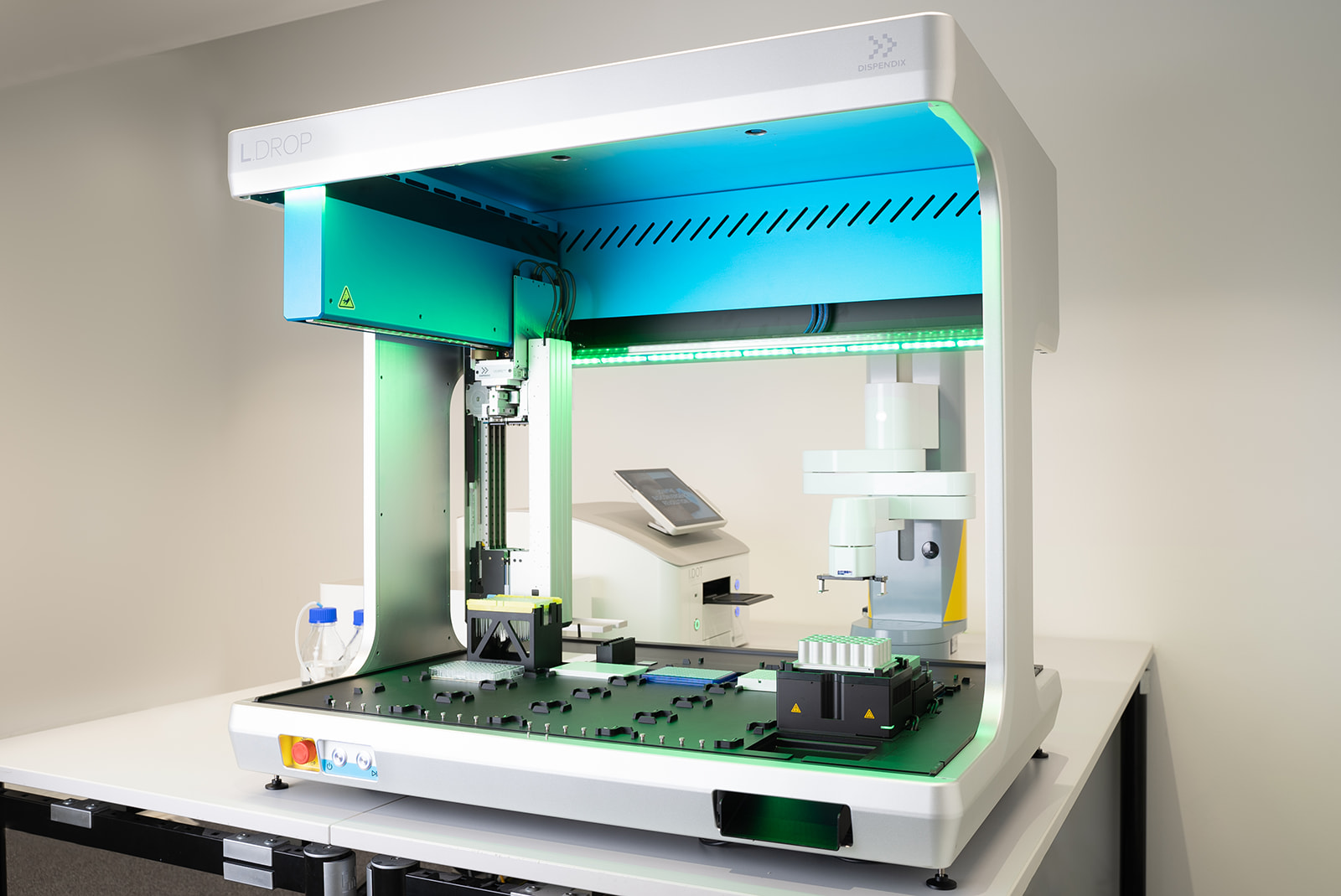

Figure 2. DISPENDIX’s G.STATION combines a robotic arm with a multichannel liquid dispenser for fully automated NGS library prep.
Automated Plate Handling Systems
Automated plate handling systems are integral to both automated and semi-automated workflows. These setups take on the burden of microplate management – handling storage, retrieval, and transport. This significantly reduces manual labor, enhancing efficiency and boosting scalability. By bringing these systems together with liquid handling robots and pipetting systems, users can develop fully streamlined workflows and achieve unparalleled lab productivity3.
Applications of Semi-Automated Pipetting
High-Throughput Screening
Semi-automation is integral to HTS efforts, where its capacity to streamline workflows, enhance efficiency, and increase scalability facilitates the rapid testing of large compound libraries in drug discovery4. Moreover, semi-automated pipetting systems enable assay miniaturization5. By reducing reaction volumes, they provide a game-changing solution in point-of-care testing and personalized medicine where samples are limited.
Omics: DNA and RNA Pipetting
In omics research, semi-automated pipetting systems stand out for their precision and accuracy6. By significantly reducing the likelihood of human error, these systems ensure volume measurements are spot-on7. The minimal human contract allows these systems to reduce the risk of DNA and RNA contamination, a critical advantage. Plus, the requirement for minimized dead volumes in automated liquid handling means researchers can make the most out of every precious drop of DNA or RNA from patient samples.
Conclusion
Semi-automated pipetting systems are essential tools that offer labs enhanced precision, scalability, and data integrity while retaining a degree of flexibility and manual control. These systems are indispensable in HTS and omics applications, where they ensure reproducibility and efficiency. Additionally, integrating advanced technologies like tip-free liquid dispensing facilitates cost reduction and sustainability. By leveraging these semi-automated pipetting solutions, labs can significantly enhance their experimental workflows, achieving high accuracy and throughput while minimizing manual labor and environmental impact.
Ready to equip your lab with enhanced accuracy and efficiency? Meet the I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser.

This sleek, compact wonder isn't just another automated non-contact liquid dispensing system. It's a game-changer designed to transform your lab with unparalleled precision, speed, and flexibility. Book a demo today and take the first step towards a faster, more efficient, and error-free lab.
References
- Torres-Acosta MA, Lye GJ, Dikicioglu D. Automated liquid-handling operations for robust, resilient, and efficient bio-based laboratory practices. Biochem Eng J. 2022;188:108713. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2022.108713
- Miller KWP, Grossman N, Haviernik P, et al. A Semi-Automated Tuberculosis Testing Workflow Reduces Manual Hazardous Sample Handling and Hands-On Time: A Proof-of-Concept Study. SLAS Technol. 2020;25(3):253-257. doi:10.1177/2472630319884519
- Markert S, Joeris K. Development of an automated, multiwell plate based screening system for suspension cell culture. BMC Proc. 2011;5(S8):O9, 1753-6561-5-S8-O9. doi:10.1186/1753-6561-5-S8-O9
- Carstens C, Elbracht R, Gärtner C, Becker H. Opportunities and limits of cell-based assay miniaturization in drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2010;5(7):673-679. doi:10.1517/17460441.2010.488264
- Pereira SAP, Dyson PJ, Saraiva MLMFS. Miniaturized technologies for high-throughput drug screening enzymatic assays and diagnostics – A review. TrAC Trends Anal Chem. 2020;126:115862. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2020.115862
- Tegally H, San JE, Giandhari J, De Oliveira T. Unlocking the efficiency of genomics laboratories with robotic liquid-handling. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):729. doi:10.1186/s12864-020-07137-1
- Christler A, Felföldi E, Mosor M, et al. Semi-automation of process analytics reduces operator effect. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2020;43(5):753-764. doi:10.1007/s00449-019-02254-y