NGS library prep automation is revolutionizing genomics, making processes more efficient, accurate, and reproducible. Critical components of this automation include magnetic bead clean-up and advanced liquid handlers, which ensure high-quality samples and streamlined workflows. This article explores the roles and benefits of these technologies in genomic research.
What Role Does Automated DNA Clean-up Play in Genomics?
Automated DNA clean-up plays a crucial role in genomics by producing high-quality samples necessary for reliable sequencing and analysis. This technology is essential in NGS library prep automation, where it removes contaminants and purifies nucleic acids prior to highly sensitive sequencing processes1. The G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device is an advanced instrument that supports magnetic bead-based clean-up for NGS library prep automation with the capacity for high-throughput processing of multiple samples simultaneously for increased lab productivity (Fig. 1). 
Figure 1. The G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device purifies DNA samples during NGS library prep automation workflows.
When combined with advanced liquid handling systems, automated workflows, like the G.PREP NGS Automation solution, can significantly enhance efficiency, accuracy, and throughput. Automated liquid handlers like the I.DOT Liquid Handler precisely dispenses small volumes of liquids, reducing human error and contamination risks, while the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device ensures that the samples are free from impurities. This synergy not only speeds up genomics workflows but also minimizes manual intervention, leading to more consistent and reliable sequencing results. Ultimately, automated DNA clean-up is indispensable for delivering high-quality, contaminant-free samples, thus enhancing the overall reliability and efficiency of genomic studies2,3.

To learn more about the essential role of automated DNA clean-up in genomics and other workflows, check out the full article.
What Role Do Automated Liquid Handlers Play in Genomics?
Automated liquid handlers play a pivotal role in genomics by significantly enhancing workflow efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility4,5. The evolution from manual pipetting to fully automated systems has transformed genomic research. While early methods were labor-intensive and prone to errors, modern liquid handlers automate the precise dispensing of reagents and samples, reducing manual errors and increasing throughput6. In genomic research, where high-throughput sequencing, gene editing, and single-cell analysis are common and scalability is essential, these tools effectively manage large volumes of samples and complex protocols.
Modern systems, such as the I.DOT Liquid Handler, uses non-contact dispensing (Fig. 2) and advanced features like DropDetection technology to ensure precise volume control and minimize contamination risks. This level of precision is crucial for reproducibility, addressing the ongoing reproducibility crisis by reducing variability and manual preparation errors7. By streamlining genomic workflows, automated liquid handlers accelerate NGS library prep automation for large-scale studies and personalized medicine, making them an invaluable tool in the modern genomics laboratory.
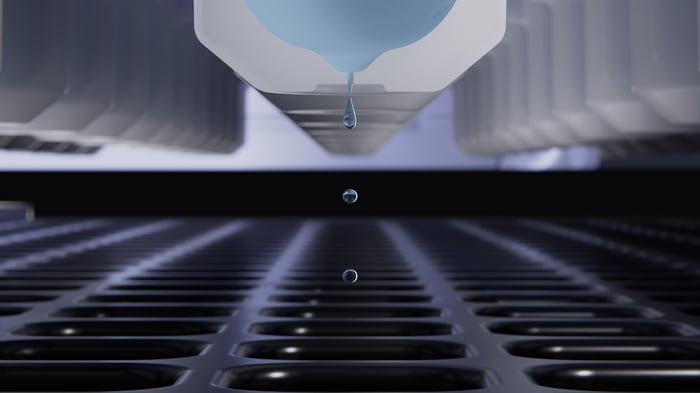
Figure 2. The I.DOT Non-Contact Dispenser facilitates tipless, contact-free liquid transfers, ideal for saving costs and the environment in NGS library prep automation pipelines.
To discover more key considerations for automated liquid handlers in genomics workflows, dive into the full article here.
What Are the Benefits and Applications of Automated Liquid Handling & DNA Clean-up?
Automated liquid handling and DNA clean-up systems offer substantial benefits for wide-ranging genomics applications. These systems increase throughput, allowing multiple samples to be processed simultaneously and accelerating workflows. Enhanced accuracy and consistency ensure uniform contamination removal, improving the quality and reliability of genomic data. Reduced manual handling frees researchers to focus on complex analytical tasks, lowers labor costs, and minimizes the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
In terms of applications, automated systems are essential in NGS library prep automation for high-throughput sequencing, genetic screening, and environmental testing. They facilitate large-scale sequencing projects, enable precise genetic screening assays in clinical diagnostics and drug discovery, and ensure high-quality DNA samples in environmental studies8–11. These systems are particularly valuable in settings where sample purity and quality are paramount, such as in rare disease diagnostics and regulatory-compliant sequencing pipelines12. By improving efficiency and accuracy, automated liquid handling and DNA clean-up systems advance the pace and reliability of scientific discoveries in genomics.
If you’re interested in learning more about the fascinating applications of automated liquid handling and DNA clean-up, our latest article can be found here.
Conclusion
Modern NGS library prep automation, driven by automated liquid handling and DNA clean-up systems, is transforming genomics by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility. These technologies ensure high-quality, contaminant-free samples and streamline workflows, accelerating scientific discoveries and applications in genomic research. Investing in these automated solutions is crucial for any laboratory aiming to improve its genomic workflows and advance the field of genomics.
Elevate your genomic research to new heights with the G.PURE NGS Clean-Up Device. Achieve unparalleled sample purity, efficiency, and reliability, ensuring that every experiment delivers accurate and reproducible results. Book a demo today!
References
- Satam H, Joshi K, Mangrolia U, et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology. 2023;12(7):997. doi:10.3390/biology12070997
- Meldrum D. Automation for Genomics, Part One: Preparation for Sequencing. Genome Res. 2000;10(8):1081-1092. doi:10.1101/gr.101400
- Meldrum D. Automation for Genomics, Part Two: Sequencers, Microarrays, and Future Trends. Genome Res. 2000;10(9):1288-1303. doi:10.1101/gr.157400
- Tegally H, San JE, Giandhari J, De Oliveira T. Unlocking the efficiency of genomics laboratories with robotic liquid-handling. BMC Genomics. 2020;21(1):729. doi:10.1186/s12864-020-07137-1
- Gaisford W. Robotic Liquid Handling and Automation in Epigenetics. SLAS Technol. 2012;17(5):327-329. doi:10.1177/2211068212457160
- Guan XL, Chang DPS, Mok ZX, Lee B. Assessing variations in manual pipetting: An under-investigated requirement of good laboratory practice. J Mass Spectrom Adv Clin Lab. 2023;30:25-29. doi:10.1016/j.jmsacl.2023.09.001
- Baker M. 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Nature. 2016;533(7604):452-454. doi:10.1038/533452a
- Itoh M, Kitsunai T, Akiyama J, et al. Automated filtration-based high-throughput plasmid preparation system. Genome Res. 1999;9(5):463-470.
- Marziali A, Willis TD, Federspiel NA, Davis RW. An automated sample preparation system for large-scale DNA sequencing. Genome Res. 1999;9(5):457-462.
- Sepulveda AJ, Birch JM, Barnhart EP, et al. Robotic environmental DNA bio-surveillance of freshwater health. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14389. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71304-3
- Nakai M, Masumoto T, Asaeda T, Rahman M. Improving the efficiency of adaptive management methods in multiple fishways using environmental DNA. Heneberg P, ed. PLOS ONE. 2024;19(4):e0301197. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0301197
- Marceddu G, Dallavilla T, Guerri G, Manara E, Chiurazzi P, Bertelli M. PipeMAGI: an integrated and validated workflow for analysis of NGS data for clinical diagnostics. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(15):6753-6765. doi:10.26355/eurrev_201908_18566